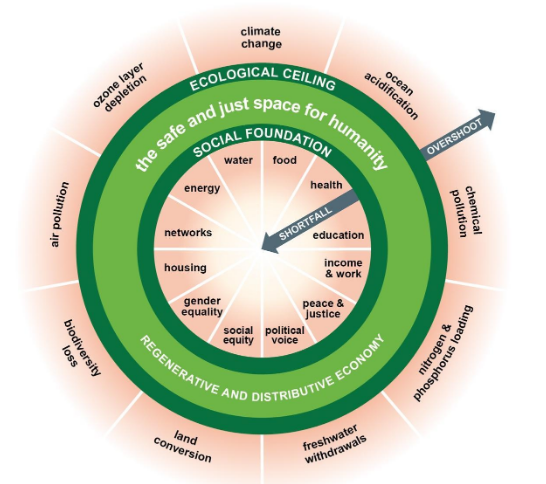
The transition towards renewable energy for a sustainable future is one of the biggest challenges facing the world today. As we face the effects of climate change, it becomes evident that we shift away from our dependence on fossil fuels and towards renewable energy technologies such as wind, solar and geothermal power. However, deploying these technologies poses ethical concerns about fair distribution and equity among different generations. The Doughnut Economy is a concept that can help us address the issues related to sustainability and fairness in our economic system. It envisions an economy that is both restorative and inclusive while staying within the earth’s ecological boundaries.

The global energy landscape is constantly evolving, driven by the search for cleaner, more efficient, and sustainable power sources. Nuclear energy has long been a controversial topic in this quest, with proponents and critics passionately arguing for and against its adoption. Hence, it is crucial for everyone who cares about the climate crisis to understand the nuclear power debate and explore the benefits, drawbacks, and future prospects of this divisive energy source.

India has set for itself rather ambitious goals and targets on the global climate platform. The third largest emitter of carbon dioxide after China, and the US in 2020, India resolved to achieve the target of Net Zero at the UN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow (COP 26), which translates to reduction in carbon emissions and not contributing to the amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere. India has further pledged to generate 50% of its electricity from non-fossil fuel sources, which amounts to around 500GW. This could lead to 45% reduction of emission intensity of the GDP (amount of GHG emissions for every unit of GDP) by 2030.

The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is surging forward as nations around the world aggressively strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. With EVs being praised as a cleaner alternative to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, the demand for lithium-ion batteries, which power most EVs, has skyrocketed. However, the environmental and social impacts of lithium mining have often been overshadowed by the EV industry's green image.

Hydropower is one of the earliest renewable sources of energy, harnessing the power of water to spin turbines and produce electricity without producing greenhouse gas emissions or other pollutants. Hydropower has the potential to play a significant role in mitigating climate change, as renewable energy sources become increasingly important in reducing carbon emissions and slowing the effects of global warming.

As the human population and world economy grow, so does the energy demand. Today, the world is grappling with the daunting task of achieving a balance between energy demand and supply. However, the current energy infrastructure is neither sufficient nor sustainable. The use of non-renewable sources like coal and oil is one of the leading causes of climate change and is unsustainable, owing to its perishability. To protect the environment and address the growing energy demands at the same time, we must shift to a more sustainable energy distribution system. And that’s where the smart grids come in.

In recent years, there has been a growing focus on electric cars as a solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. Governments around the world are offering incentives to encourage consumers to switch to electric cars, and the media is filled with stories about new electric car models and charging infrastructure.

Climate change is not a distant threat looming on the horizon! The world is facing more and more damaging storms, floods, and droughts, which makes us think that the earth is running out of time to heal and protect itself. India needs to step up its efforts in both adaptation and mitigation, from short-term crisis reaction to long-term planning, if it wants to do something big, like reaching its net-zero emissions goal by 2070.

India is aiming to achieve the net-zero target by 2070, which was recently emphasized during the COP27 conference held in Egypt. Indian Environment Minister Bhupendra Singh delivered the official statement at the COP27 summit, and highlighted that PM Modi announced India’s aim of achieving net zero emissions by 2070 at Glasgow, and that India is escalating its efforts towards achieving the same. “Within one year, India has submitted its Long-Term Low Emissions Growth Strategy indicating low carbon transition pathways in key economic sectors”, he added.

Every part of the world is being affected by the ongoing climate disaster, which is getting worse at the fastest rate known in human history. The world economy has been hurt by climate change, which includes rising sea levels, rising temperatures, and more frequent disasters like floods, wildfires, and droughts. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) sixth assessment report, which came out in April 2022, talked a lot about how important climate technology is because it can help lower the chance of climate change effects happening again. It is a UN group whose job it is to do scientific evaluations on climate change and its effects, as well as possible future risks and ways to deal with them. Since it was founded in 1988, the IPCC has put out a number of studies on climate change. In this age of technology, we need new technical methods right away to help people adapt to and lessen the effects of climate change. The study stressed that we can slow down climate change by using technical interventions.