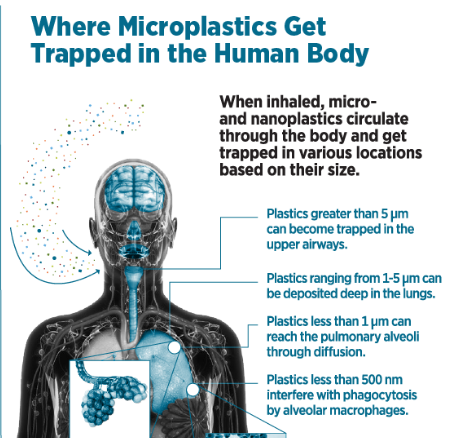
A new and alarming form of air pollution is emerging across India’s urban centers — invisible to the naked eye but potentially dangerous to every breath we take. Recent scientific findings reveal that microscopic plastic particles, known as inhalable microplastics (iMPs), are now part of the air we breathe. This new contaminant adds a disturbing layer to India’s already critical air-quality crisis.

We hear about exciting technologies like self-driving cars and facial recognition, but there’s more to AI than that. Our society has undergone a massive technological revolution over the past decade and electronic appliances have now become ubiquitous.

Hey there, tech enthusiasts! Let's talk about something super important in our digital lives – what happens when we say goodbye to our trusty gadgets. You know, the old smartphones, tablets, and laptops that have been with us through thick and thin. Turns out, there's more to it than just tossing them away. Did you ever think about your stuff stored on these devices? Like photos, messages, and all those bits and pieces of your life. Well, it's time to dive into the world of e-waste and data security, where keeping our info safe is the name of the game.

India is a major contributor to the global e-waste crisis. Between 2010 and 2022, India experienced the highest global growth of 163% in generating electronic waste (e-waste) from screens, computers, and small IT and telecommunication equipment (SCSIT), according to a United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) report.

These days, it’s hard to imagine life without electronic devices. From smartphones and laptops to medical tools, we rely on electronics for just about everything. However, as the demand for new gadgets continues to rise, so does the volume of electronic waste. And that’s become a huge problem. As we keep producing more devices, we also need to find better ways to manage the waste they leave behind, so we don’t harm the environment and can reuse valuable materials.

E-waste is a growing problem, with millions of old phones, computers, and other devices being thrown away every year. Proper disposal methods are often neglected and recycling rates remain low, with only 20% of e-waste properly handled worldwide. This gap between disposal and recycling is where Closing the Loop steps in.

We've all used ATMs to withdraw cash using our debit cards, and over the past few decades, vending machines have also popped up that dispense everything from chocolates to snacks. But have you ever heard of a machine or a kiosk that gives you instant cash in exchange for your old electronics, like mobile phones? Pretty cool, isn’t it?

Toys play a crucial role in a child's life. Toys allow children to develop their imaginations, as well as their fine and gross motor skills. They also help them build interpersonal skills such as sharing and problem-solving. Toys are not just fun; they're essential tools for a child's growth and development.

Bharati Chaturvedi is a name you may not hear every day, but her work has quietly reshaped how India manages its waste, particularly e-waste. She founded the Chintan Environmental Research and Action Group in 1999 with the motive of turning waste into opportunity. What makes her work stand out is her focus on the people who often go unnoticed, the informal waste pickers who play a critical role in keeping our cities cleaner but rarely get the recognition they deserve.

Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a growing problem in many parts of the world, and India is no exception. Our country produces over 3.2 million tonnes of e-waste annually, and Nagaland, like many other regions, has seen a sharp rise in electronics usage without a formal system to deal with the waste. E-waste includes everything from mobile phones to refrigerators which contain hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium that can cause environmental and health problems if disposed of improperly. The hazardous substances can seep into soil and water and contaminate local ecosystems.