Combining environmental education with urban greening efforts, we inspire the next generation and create dense, carbon-capturing forests in our cities to combat climate change
Empowering readers with in-depth insights into climate change, innovative solutions, and sustainable practices to foster informed eco-friendly actions.
Reducing emissions to pave the way for a sustainable future where GHG emissions are equal to GHG sequestration. Pathways for achieving carbon-neutrality and exploring energy-efficient solutions across various sectors including energy, transportation, agriculture, and construction.
Climate change has emerged as one of the most pressing challenges of the 21st century, impacting ecosystems, economies, and communities across the globe. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and ecological imbalances are no longer distant threats—they are current realities. In this context, India is increasingly turning to technological innovation, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI), to address climate challenges and build resilience for the future. India’s approach to climate action reflects a balance between development and sustainability. Over the years, the country has made notable progress by expanding renewable energy capacity, increasing green cover, and implementing policies aimed at reducing emissions. However, as climate risks intensify, traditional methods alone are no longer sufficient.

Exploring renewable energy (wind, solar, hydro, H₂) alternatives to fossil fuels to achieve carbon-neutrality goals. Ways to reduce the dependency on conventional fuels and building renewable energy capacity.
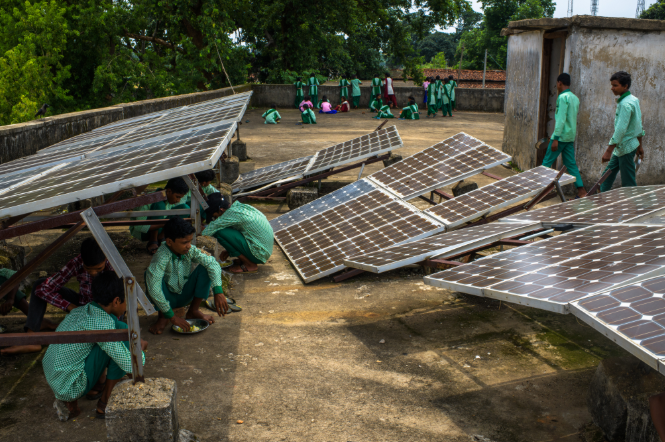
In the far-flung hills of Manipur, where winding roads and rugged terrain often keep communities cut off from reliable infrastructure, electricity has long been a distant dream. For many households, darkness would fall early—not just at sunset, but on opportunities for education, livelihoods, and progress. However, one man’s vision has begun to rewrite this narrative. Seth Moirangthem, through his initiative SNL Energy Solutions, is bringing light—both literal and transformative—to some of the most underserved regions of Northeast India.

Understanding the challenges and opportunities with e-Waste and its management across the world. Innovative solutions to reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle e-waste to generate income and employment.
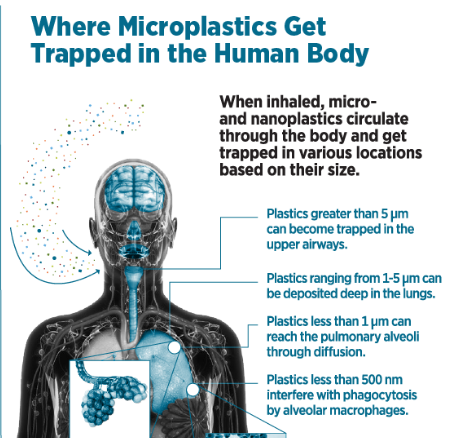
A new and alarming form of air pollution is emerging across India’s urban centers — invisible to the naked eye but potentially dangerous to every breath we take. Recent scientific findings reveal that microscopic plastic particles, known as inhalable microplastics (iMPs), are now part of the air we breathe. This new contaminant adds a disturbing layer to India’s already critical air-quality crisis.

At the India AI Impact Conference 2026 held at Bharat Mandapam, New Delhi, Meghalaya emerged as a forward-looking state by presenting its initiatives in AI-led governance and climate action. The conference, part of India’s broader push to position ...

At the “Technology and Innovation Conclave 2.0” held in New Delhi, Union Minister of State for Science and Technology and Earth Sciences, Dr Jitendra Singh, reiterated that combating climate change is a global imperative that no single country ca...
Rapid urbanization and growing urban affluence tend to have profound environmental consequences causing threat to human beings and the environment. Prolonged ignorance of the ecological feedback is affecting every living and non-living element on Earth. The human ecosystem is bearing the brunt in matters of health, city and regional problems, disrupting social structure, economic inequalities as well as global sustainability. Such environmental changes are distinctly visible in rapidly growing Indian cities and urban agglomerations and even rural regions. Excessive land and air pollution, increased carbon footprint owing to fossil fuel-based energy use, deforestation, depleting water quality, problems of electronic waste disposal, declining population of flora and fauna – to name a few.
